The Most Popular Historical Events in the World
History is filled with remarkable events that have shaped our world. From ancient civilizations to modern times, certain events stand out due to their profound impact. Here’s an easy-to-understand overview of some of the most popular historical events that have captured the attention of people around the globe.
The Birth of Civilizations
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt, with its majestic pyramids, pharaohs, and the Sphinx, is one of the most fascinating civilizations. It began around 3100 BC and lasted for over 3,000 years. The Egyptians were known for their advancements in writing, architecture, and art. The construction of the pyramids, especially the Great Pyramid of Giza, remains a marvel of engineering. Egyptian society was highly organized, with a strong emphasis on religion and the afterlife.
Mesopotamia
Often referred to as the “Cradle of Civilization,” Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) was home to the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. It is here that writing, in the form of cuneiform script, was invented, and the first cities were built. The Code of Hammurabi, one of the earliest known sets of laws, originated in Mesopotamia. This region also saw significant advancements in mathematics, astronomy, and literature, including the famous Epic of Gilgamesh.
Classical Antiquity
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is known for its contributions to philosophy, democracy, and the arts. The period from the 8th century BC to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC saw the rise of city-states like Athens and Sparta and philosophers such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. Greek mythology, theater, and the Olympic Games also have their origins in this period. The Greeks made significant advances in science, mathematics, and politics, laying the groundwork for Western civilization.
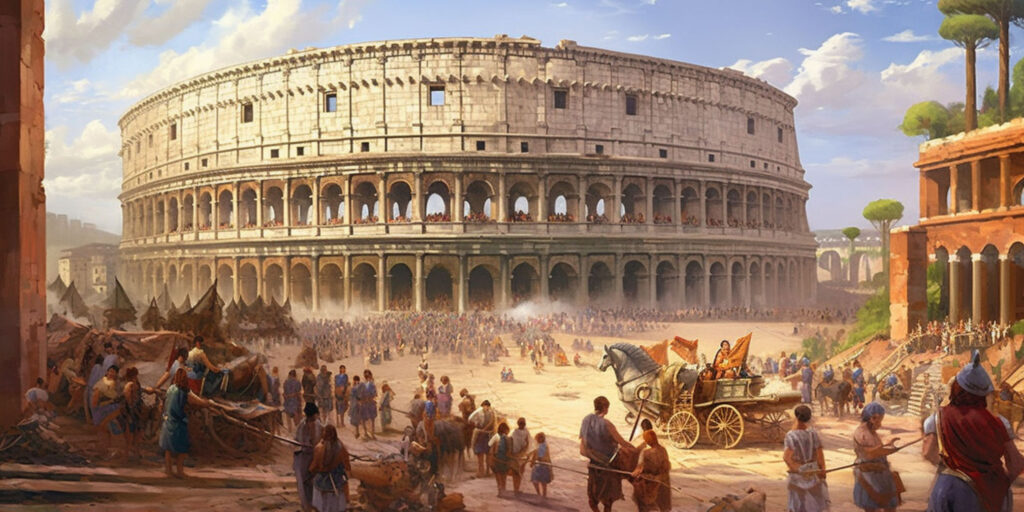
The Roman Empire
The Roman Empire, which began in 27 BC and lasted until AD 476, was one of the largest empires in history. It left a lasting legacy on law, politics, architecture, and language. The Romans built extensive road networks and aqueducts and spread their culture across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. The Pax Romana, a period of relative peace and stability, allowed for economic growth and cultural exchange. The fall of Rome marked the end of ancient history and the beginning of the Middle Ages.
The Middle Ages
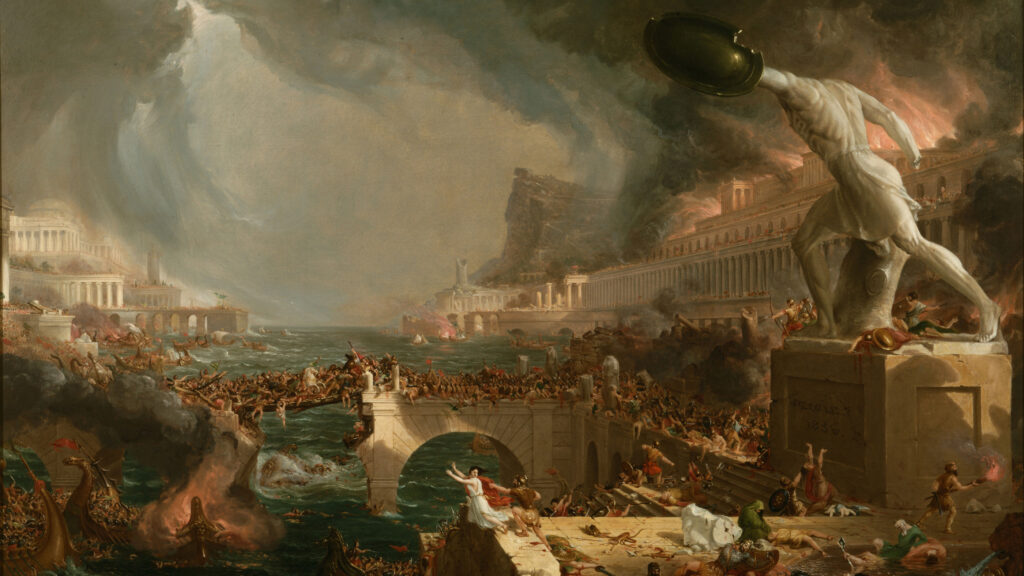
The Fall of Rome
The fall of the Western Roman Empire in AD 476 marked the beginning of the Middle Ages. This period, also known as the Dark Ages, saw the rise of feudalism, the spread of Christianity, and the emergence of powerful kingdoms and empires in Europe. The Byzantine Empire continued to thrive in the east, preserving much of Roman and Greek culture. The Middle Ages were also characterized by the rise of monasticism, which played a crucial role in preserving knowledge and education.
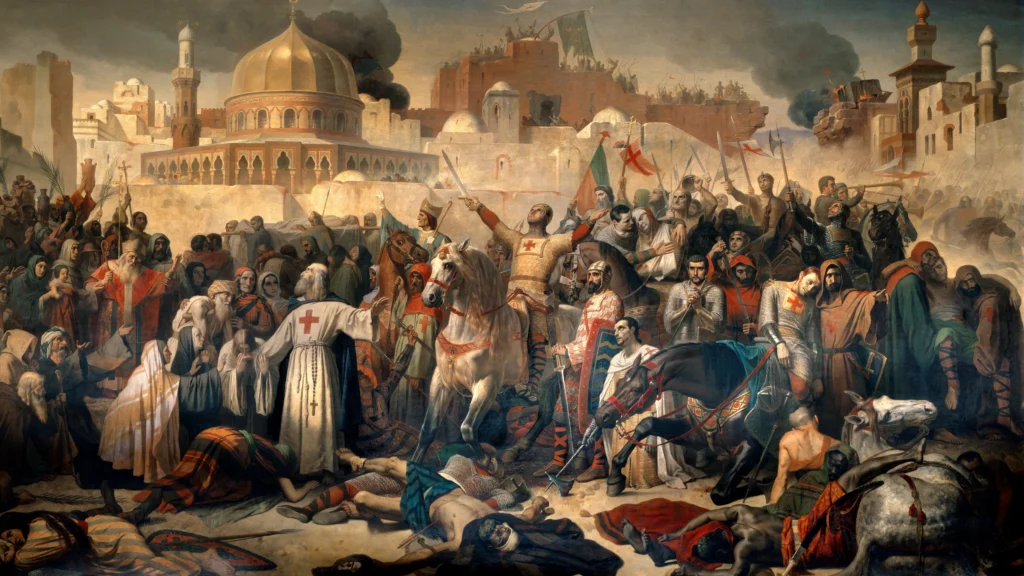
The Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars between Christians and Muslims over control of the Holy Land, spanning from 1096 to 1291. These wars had significant cultural, economic, and political impacts on Europe and the Middle East. The Crusades led to increased trade between Europe and the East, the transfer of knowledge and technology, and the growth of cities. They also left a legacy of religious conflict and cultural exchange.
The Renaissance and Exploration
The Renaissance
The Renaissance, which began in the 14th century in Italy, was a period of renewed interest in art, science, and literature. Figures like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Galileo Galilei made significant contributions that shaped the modern world. The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the mid-15th century revolutionized the spread of knowledge. The Renaissance emphasized humanism, individualism, and secularism, leading to a cultural rebirth and the questioning of traditional authority.
The Age of Exploration
From the 15th to the 17th centuries, European explorers like Christopher Columbus, Vasco da Gama, and Ferdinand Magellan set out on voyages that expanded the known world. Their discoveries led to the establishment of trade routes and the colonization of the Americas, Africa, and Asia. This era brought about significant cultural exchanges, the spread of diseases that decimated indigenous populations, and the transatlantic slave trade. The Age of Exploration fundamentally changed the global economy and geopolitics.
The Modern Era
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which began in Britain in the late 18th century, transformed societies from agrarian economies to industrial powerhouses. Innovations like the steam engine, spinning jenny, and power loom revolutionized manufacturing and transportation. Urbanization increased as people moved to cities for work, leading to significant social changes. The Industrial Revolution also spurred technological advancements, economic growth, and improved standards of living, but it also brought about challenging working conditions and environmental impacts.
The American Revolution
The American Revolution (1775-1783) was a pivotal event in world history. It resulted in the thirteen American colonies gaining independence from Britain and the establishment of the United States of America. The revolution was inspired by Enlightenment ideas of liberty and democracy. Key figures like George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, and Benjamin Franklin played essential roles. The American Revolution influenced other countries to pursue independence and democratic ideals.
The French Revolution
The French Revolution (1789-1799) was a period of radical social and political change in France. It led to the overthrow of the monarchy, the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte, and the spread of revolutionary ideas across Europe. The revolution challenged the traditional social hierarchy and promoted ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity. It also led to significant changes in French society, including the abolition of feudal privileges and the establishment of a republic.
The 20th Century
World War I
World War I (1914-1918) was a devastating global conflict that involved many of the world’s great powers. The war resulted in significant loss of life, the redrawing of national borders, and set the stage for World War II. New technologies and warfare tactics, such as trench warfare, machine guns, and chemical weapons, caused unprecedented destruction. The Treaty of Versailles, which ended the war, imposed harsh penalties on Germany, leading to economic hardship and political instability.
World War II
World War II (1939-1945) was the deadliest conflict in human history, involving most of the world’s nations. The war saw the rise and fall of Adolf Hitler, the Holocaust, and the use of atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. It resulted in the establishment of the United Nations and the beginning of the Cold War. The war led to significant geopolitical changes, the emergence of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers, and the decolonization of Asia and Africa.
The Civil Rights Movement
The Civil Rights Movement in the United States, which gained momentum in the 1950s and 1960s, was a struggle for social justice and equality for African Americans. Leaders like Martin Luther King Jr. and Rosa Parks played crucial roles in challenging segregation and discrimination. The movement led to landmark legislation, such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, which aimed to end racial discrimination and ensure equal rights for all Americans.
The Contemporary World
The Fall of the Berlin Wall
The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 symbolized the end of the Cold War and the division between East and West Germany. It marked the beginning of a new era of freedom and democracy in Eastern Europe. The reunification of Germany and the collapse of communist regimes in Eastern Europe paved the way for the expansion of the European Union and NATO, as well as significant political, economic, and social changes.
The Digital Revolution
The late 20th and early 21st centuries have seen the rise of the Digital Revolution, characterized by the development of computers, the internet, and digital technologies. This revolution has transformed how we communicate, work, and live. Innovations such as smartphones, social media, and artificial intelligence have created new opportunities and challenges, reshaping industries and influencing every aspect of modern life.
Conclusion
History is a tapestry of interconnected events that have shaped our world. From ancient civilizations to modern revolutions, each era has contributed to the progress and development of humanity. Understanding these events helps us appreciate the complexities of our past and the possibilities of our future.