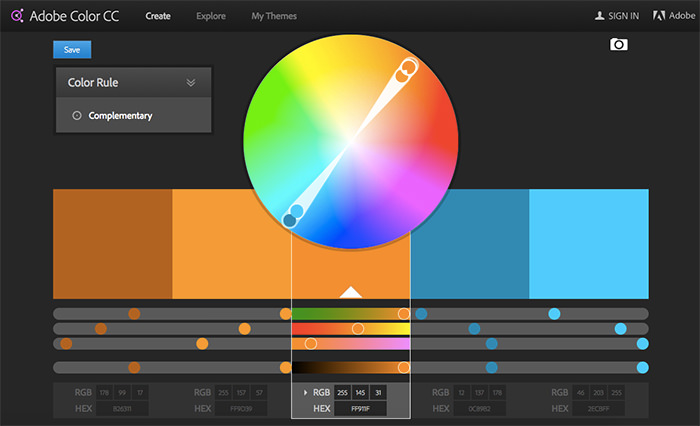
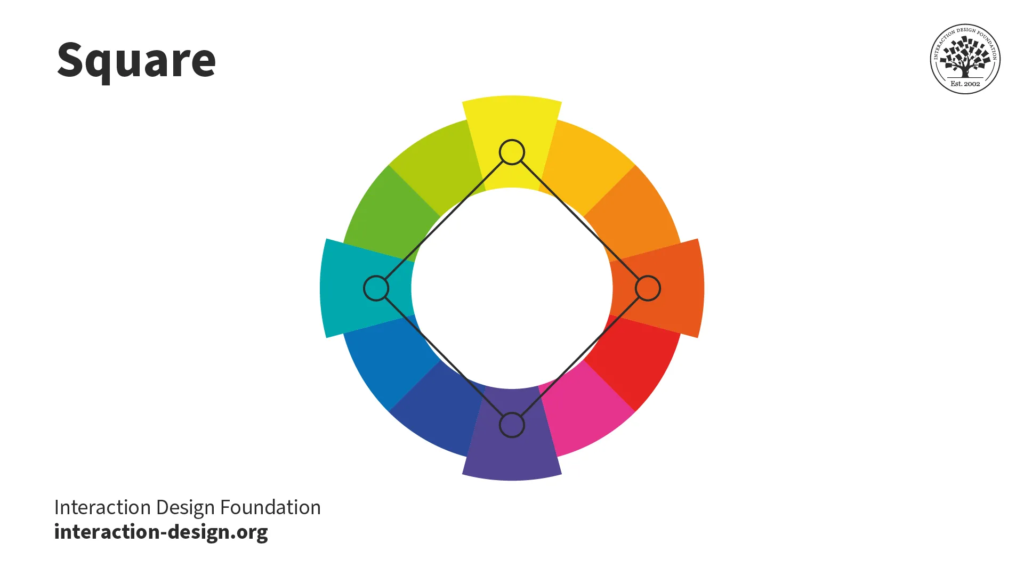
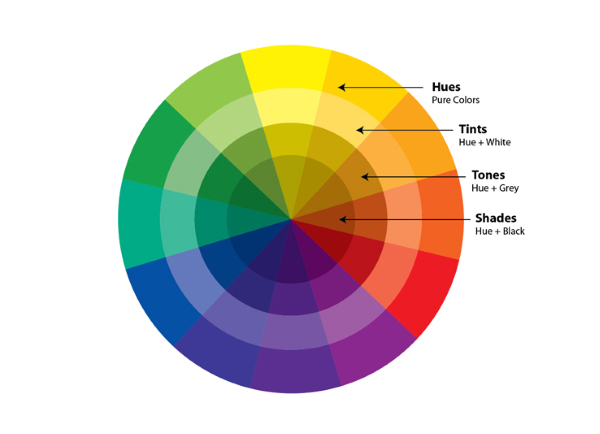
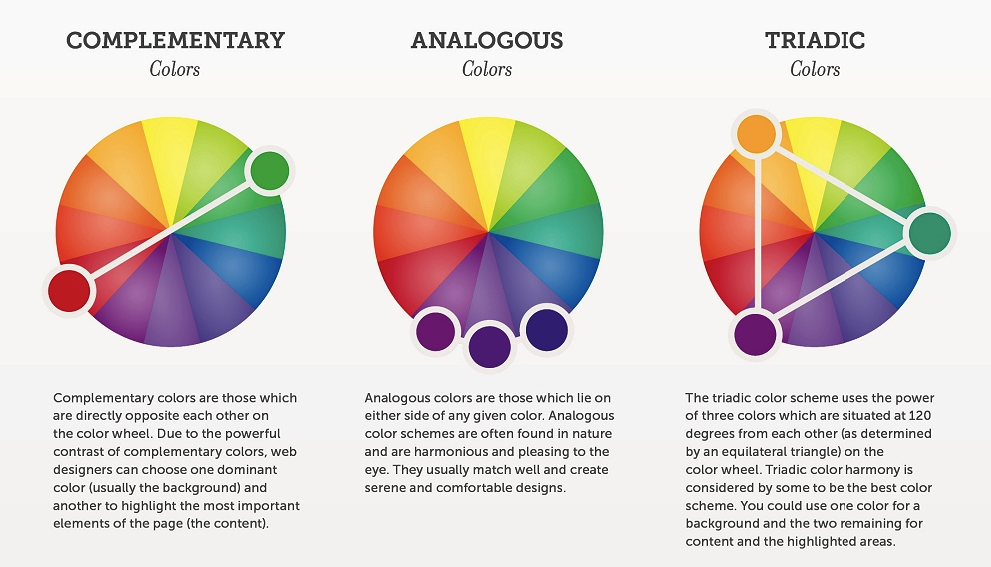
Cultural and Contextual Considerations for Web Design In the interconnected global landscape of the internet, web design has evolved beyond mere aesthetics to encompass cultural and contextual considerations. As the online audience becomes increasingly diverse, understanding the cultural nuances and contextual factors that influence user behavior and perceptions is essential for creating inclusive and effective web experiences. In this article, we explore the significance of cultural and contextual considerations in web design, along with practical strategies for implementing them. Understanding Cultural Diversity Cultural diversity refers to the variety of cultural perspectives, practices, and values that exist within a society or community. In the context of web design, cultural diversity manifests in various ways, including language, symbolism, color preferences, social norms, and user expectations. Designers must recognize and respect these cultural differences to ensure that their websites are accessible and engaging to a global audience. Language and Communication Language is a fundamental aspect of culture and plays a crucial role in effective communication on the web. Designers should consider the linguistic diversity of their target audience and provide multilingual options when appropriate. This includes not only translating textual content but also adapting cultural references, idiomatic expressions, and colloquialisms to resonate with different language speakers. Symbolism and Imagery Symbols and imagery often carry cultural meanings and associations that may vary across different societies and regions. Designers should be mindful of using culturally sensitive symbols, icons, and visuals to avoid unintentionally offending or alienating users. Conducting research or consulting with local experts can help ensure that imagery is culturally appropriate and resonates with the target audience. Color Symbolism Colors hold symbolic significance in many cultures and can evoke different emotions and perceptions. For example, while white may symbolize purity and peace in Western cultures, it may represent mourning or death in some Asian cultures. Designers should be cognizant of cultural color associations and consider how color choices may be interpreted by diverse audiences. Adapting to Contextual Factors In addition to cultural considerations, web design must also account for contextual factors that influence user interaction and engagement. Contextual factors encompass the user’s environment, situation, device, and browsing context, all of which shape their online experience. By understanding these contextual variables, designers can create more relevant and user-centric web interfaces. Device and Platform Diversity Users access the web through a myriad of devices and platforms, including desktop computers, smartphones, tablets, and smart TVs. Each device has its own screen size, resolution, input method, and capabilities, which can impact how users interact with websites. Designers should embrace responsive design principles to ensure that websites adapt seamlessly to different devices and provide a consistent user experience across platforms. Browsing Context The context in which users access a website can influence their behavior and expectations. For instance, users browsing on-the-go may have different needs and preferences compared to those browsing from the comfort of their homes. Designers should consider the user’s context, such as their location, time of day, and task at hand, to tailor the website experience accordingly. Accessibility and Inclusivity Accessibility is a critical aspect of web design that ensures equal access and usability for all users, including those with disabilities. Designers should adhere to web accessibility standards, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), to accommodate users with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments. This includes providing alternative text for images, keyboard navigation support, and semantic HTML markup. Practical Strategies for Implementation Implementing cultural and contextual considerations in web design requires a proactive and holistic approach. Here are some practical strategies for integrating these considerations into the design process: Conduct User Research Before designing a website, conduct thorough user research to understand the cultural backgrounds, preferences, and behaviors of the target audience. Use surveys, interviews, and usability testing to gather insights and validate design decisions. Collaborate with Local Experts Engage with cultural experts, translators, and native speakers to ensure cultural authenticity and sensitivity in content creation and design. Their expertise can help identify potential cultural pitfalls and provide valuable insights into local customs and norms. Test Across Different Contexts Test the website across various contexts, devices, and user scenarios to identify usability issues and opportunities for improvement. Consider conducting usability testing in different geographical locations to capture diverse perspectives and feedback. Iterate and Adapt Web design is an iterative process, and ongoing adaptation is essential for staying responsive to cultural shifts and evolving user needs. Monitor website analytics, gather user feedback, and iteratively refine the design to enhance cultural relevance and usability. Conclusion In today’s multicultural and digitally interconnected world, cultural and contextual considerations play a pivotal role in shaping successful web experiences. By embracing cultural diversity, understanding contextual factors, and implementing inclusive design practices, designers can create websites that resonate with diverse audiences and foster meaningful engagement. By prioritizing cultural and contextual considerations, web design can transcend boundaries and bridge cultural divides, ultimately enriching the online experience for all users.