Mastering Web Layout Foundation Principles: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of web design, mastering the foundation principles of layout is akin to laying a solid groundwork for constructing a masterpiece. A well-executed layout not only enhances the visual appeal of a website but also plays a pivotal role in guiding users seamlessly through content. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the core principles that underpin effective web layout design, providing you with a deep understanding and practical insights to elevate your skills.
Understanding Web Layout Foundation Principles
1. Typography Mastery
Typography serves as the backbone of web design, influencing readability, hierarchy, and overall aesthetic appeal. To master typography in web layout:
- Font Selection: Choose fonts that align with the website’s tone and purpose. Strive for a harmonious blend of serif and sans-serif fonts for enhanced readability.
- Hierarchy: Establish a clear hierarchy through variations in font size, weight, and style. Use larger, bolder fonts for headings and subheadings to denote importance.
- Line Length and Spacing: Optimize line length and spacing to ensure comfortable reading experiences across devices. Aim for a line length of 45-75 characters and generous line spacing for improved legibility.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in typography throughout the website to reinforce brand identity and coherence.
2. Color Theory Application
Color plays a crucial role in evoking emotions, establishing visual hierarchy, and conveying brand identity. To leverage color effectively in web layout:
- Color Psychology: Familiarize yourself with the psychological associations of different colors. For instance, blue conveys trust and professionalism, while red evokes passion and urgency.
- Color Contrast: Ensure sufficient contrast between text and background colors to enhance readability, particularly for users with visual impairments. Use tools like WCAG Contrast Checker to validate color contrast ratios.
- Color Schemes: Experiment with various color schemes, such as complementary, analogous, and monochromatic, to create visually appealing palettes that resonate with the website’s purpose and audience.
- Brand Consistency: Align color choices with the brand’s visual identity and guidelines to maintain consistency across digital touchpoints.
3. Layout Composition Principles
Layout composition governs the arrangement of visual elements on a web page, influencing navigation, engagement, and user experience. To master layout composition:
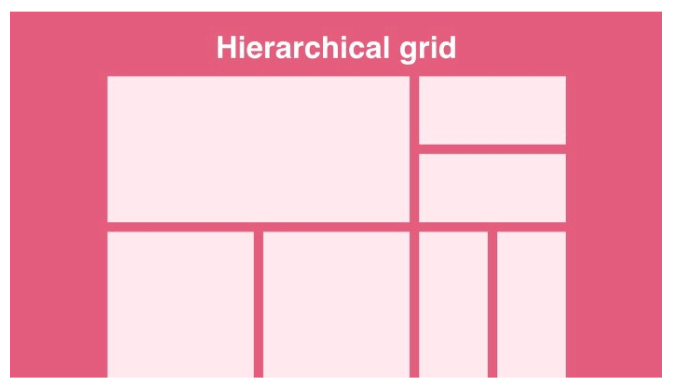
- Grid Systems: Embrace grid-based layouts to achieve consistency, alignment, and balance. Grid systems provide a framework for organizing content and maintaining visual harmony.
- Whitespace Utilization: Harness the power of whitespace to enhance visual clarity, emphasize key elements, and improve user focus. Strategic use of whitespace creates breathing room and reduces cognitive overload.
- Visual Hierarchy: Establish a clear visual hierarchy by organizing content based on importance. Employ techniques such as size, color, contrast, and placement to guide users’ attention and facilitate navigation.
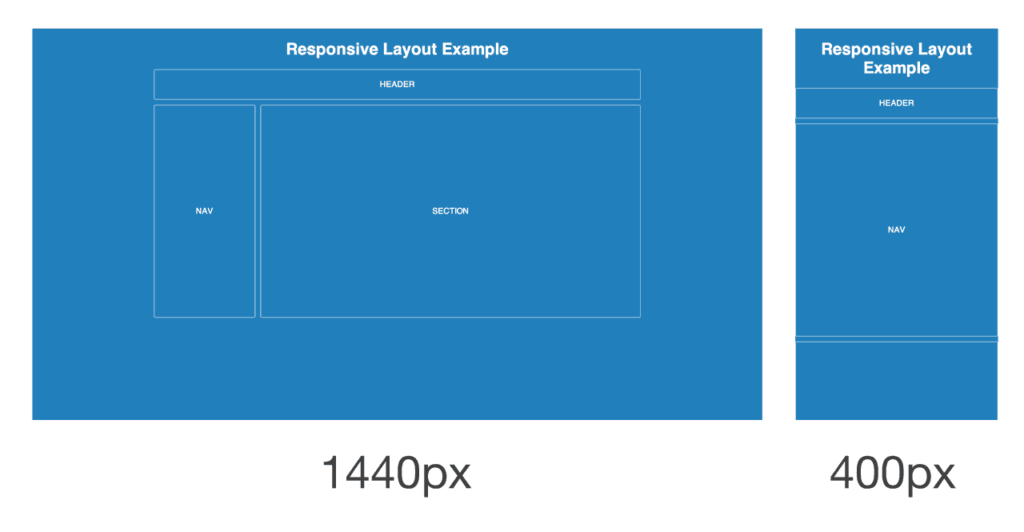
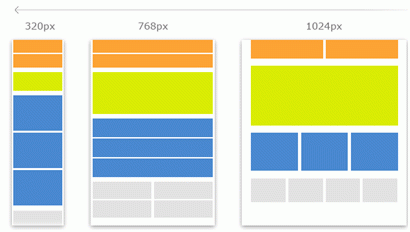
- Responsive Design Integration: Incorporate responsive design principles to ensure seamless experiences across devices. Utilize flexible grids, fluid images, and media queries to adapt layouts to varying screen sizes and resolutions.
4. Accessibility Integration
Accessibility is paramount in web design, ensuring that websites are inclusive and usable by individuals of all abilities. To prioritize accessibility in web layout:
- Semantic HTML: Utilize semantic HTML elements to enhance screen reader compatibility and provide meaningful structure to content.
- Alt Text for Images: Always include descriptive alt text for images to assist users with visual impairments in understanding the content.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure that all interactive elements are accessible via keyboard navigation, allowing users to navigate the website without relying on a mouse.
- Color Contrast: Maintain sufficient color contrast between text and background elements to accommodate users with visual impairments.
- Responsive Design: Implement responsive design techniques to optimize layouts for assistive technologies and various viewport sizes.
Practical Implementation and Continued Learning
1. Hands-On Practice:
- Apply the foundation principles of web layout in real-world projects, such as designing personal portfolios, blogs, or e-commerce websites.
- Experiment with different typography treatments, color schemes, and layout compositions to refine your skills and discover your design style.
2. Seek Feedback and Iterate:
- Share your work with peers, mentors, or online communities to solicit constructive feedback and insights.
- Iterate on your designs based on feedback, user testing, and ongoing learning to continuously improve and grow as a designer.
3. Stay Updated and Inspired:
- Stay abreast of emerging trends, best practices, and new tools in web design by following industry blogs, attending conferences, and participating in online forums.
- Draw inspiration from renowned designers, design showcases, and award-winning websites to fuel your creativity and expand your design repertoire.
Conclusion
Mastering the foundation principles of web layout is essential for creating visually captivating, user-friendly, and accessible websites. By understanding typography mastery, color theory application, layout composition principles, and accessibility integration, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and skills to craft exceptional web experiences. Through practical implementation, continuous learning, and a passion for design, you’ll embark on a journey of growth, innovation, and excellence in the dynamic field of web design.